Daily Current Affairs
To The Point Notes
Polity
1.Juvenile Justice Board (JJB)
Established: After the enactment of the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2000 (earlier Juvenile Court)
Legal Basis: Section 4 (1) of the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015
Composition:
- One Metropolitan Magistrate or Judicial Magistrate (First Class) with minimum 3 years experience
- Two Social Workers (one mandatory woman)
Authority: State Government
- Each district requires one or more JJBs
- State Governments/UT Administrations are responsible for setting up JJBs
Definition of Child (as per Act):
- A person under 18 years of age (Section 2(12))
Two Categories of Children under the Act:
- Child in Conflict with Law: Committed an offence
- Child in Need of Care and Protection: Victim of crime or unfortunate circumstances
Functions of JJB:
- Address cases involving juveniles in conflict with the law.
- Ensure the child’s rights are protected throughout (apprehension, inquiry, aftercare, rehabilitation).
- Facilitate legal aid through legal services institutions.
- Conduct monthly inspections of residential facilities for children in conflict with law (Observation Homes & Special Homes). Recommend improvements to District Child Protection Unit and state government.
Economy
2.Reserve Bank of India’s Economic Capital Framework (ECF)
Context:
- RBI transferred a surplus of Rs 2.11 lakh crore to the government (FY 2023-24) based on the ECF.
About ECF:
- Adopted in 2019 following recommendations by the Bimal Jalan committee.
- Determines the appropriate level of:
- Risk provisions
- Profit distribution to the government (as per RBI Act, 1934 Section 47)
Key Points:
- ECF ensures the RBI maintains:
- Adequate reserves for potential financial risks
- Transfers remaining profits to the government
Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB):
- Increased to 6.5% for FY 2023-24 (from 6% previously).
- Represents a buffer within the ECF to manage potential financial risks.
- Committee recommendation: Maintain CRB between 6.5% – 5.5% of RBI’s balance sheet.
Economy
3.Competition Commission of India (CCI)
Established: 2009 (by the Government of India under the Competition Act, 2002)
Ministry: Ministry of Corporate Affairs
Body Type: Statutory, Quasi-judicial
Members: Chairperson and up to 6 Members appointed by the Central Government
Objectives
- Eliminate anti-competitive practices
- Promote and sustain fair competition
- Protect consumer interests
- Ensure freedom of trade in Indian markets
Powers and Responsibilities
- Enforce and implement the Competition Act (2002)
- Investigate anti-competitive agreements
- Investigate abuse of dominant market position
- Regulate mergers, acquisitions, and amalgamations to prevent adverse effects on competition
Recent Context (15th Annual Day)
- The Attorney General for India emphasized the need to balance free market principles with social welfare goals.
Source : https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=2021147
Science and Technology
4.Electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) Aircraft
What is it?
- An electric aircraft that can hover, take off, and land vertically using electric motors.
- A new technology in urban air mobility.
Features:
- Low-altitude, short-range flights within cities.
- Carries a small number of passengers (typically 4-8).
Technology:
- Distributed electric propulsion: Multiple electric motors integrated into the aircraft for efficiency and safety.
- Driven by advancements in electric motors, batteries, and control systems.
Applications:
- Air taxi services
- Delivery drones
- Emergency medical transport
- Cargo transport
- Recreational flying
Benefits:
- Improved urban mobility and connectivity within and between cities.
- Potential to reduce traffic congestion.
- On-demand transportation options.
Current Status in India:
- ePlane Company (IIT Madras) developing eVTOL taxis for launch in Bengaluru (2024).
- Indian government regulations for eVTOL use are still under development.
Geography
5.La Niña and Al Nino
La Niña: The “Cold Sister”
Context:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD) predicts above-average monsoon rains due to La Niña conditions expected in August-September.
El Niño & La Niña:
- Ocean-atmosphere interactions impacting Pacific Ocean temperatures.
- El Niño (more frequent) – Warmer waters in eastern Pacific.
- La Niña (less frequent) – Colder waters in eastern Pacific.
Normal Conditions:
- Trade winds blow west, pushing warm surface water from South America to Asia (upwelling of cold water near South America).
- Warm surface water near Indonesia creates low pressure, leading to cloud formation and rainfall (monsoon development).
La Niña (The Cold Sister):
- Stronger trade winds push warm water towards Indonesia, cooling the eastern Pacific.
Impacts:
- Increased Rainfall: Southeast Asia, northern Australia, parts of South America (India – except east/northeast).
- Drier Conditions: Southwestern US, parts of Africa (droughts).
- Stronger Atlantic Hurricanes: Reduced wind shear allows for more hurricane formation (e.g., record 30 in 2021).
- Cooler Temperatures: Pacific Northwest US, parts of South America.
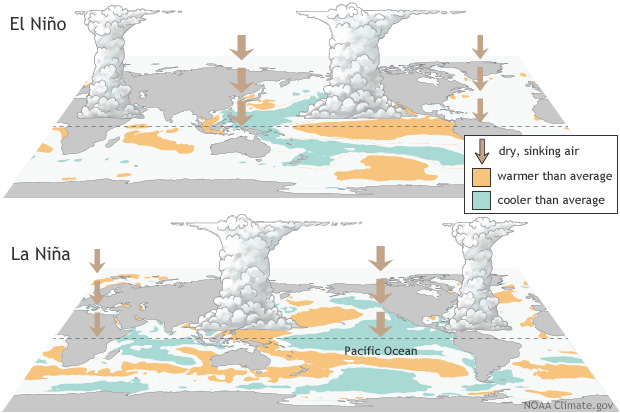
El Niño: The “Little Boy”
Origin:
- Spanish term meaning “Little Boy.”
- Noticed by South American fishermen in the 1600s due to unusually warm Pacific waters.
El Niño Events:
- Warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Weakening trade winds push warm water eastward.
Impact on India:
- Reduced Monsoon Rainfall: Droughts in many parts of the country, impacting agriculture, water resources, and the economy.
- Increased Temperatures: Rise in temperatures across India.
- Forest Fires: Drier conditions heighten risk of fires, causing environmental damage, biodiversity loss, and air pollution.
- Water Scarcity: Decreased rainfall leads to water scarcity for drinking, irrigation, and hydropower generation.
- Fisheries Impact: Changes in sea temperatures and currents disrupt fish migration patterns and populations.
El Niño and Climate Change:
- Scientists believe climate change may:
- Alter average Pacific Ocean conditions.
- Increase the frequency of El Niño events.
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO) suggests climate change may affect:
- Intensity of extreme weather events.
- Frequency of El Niño and La Niña related events.



 हिन्दी
हिन्दी